创建pod沙箱
这里的pod沙箱其实就是pod pause容器
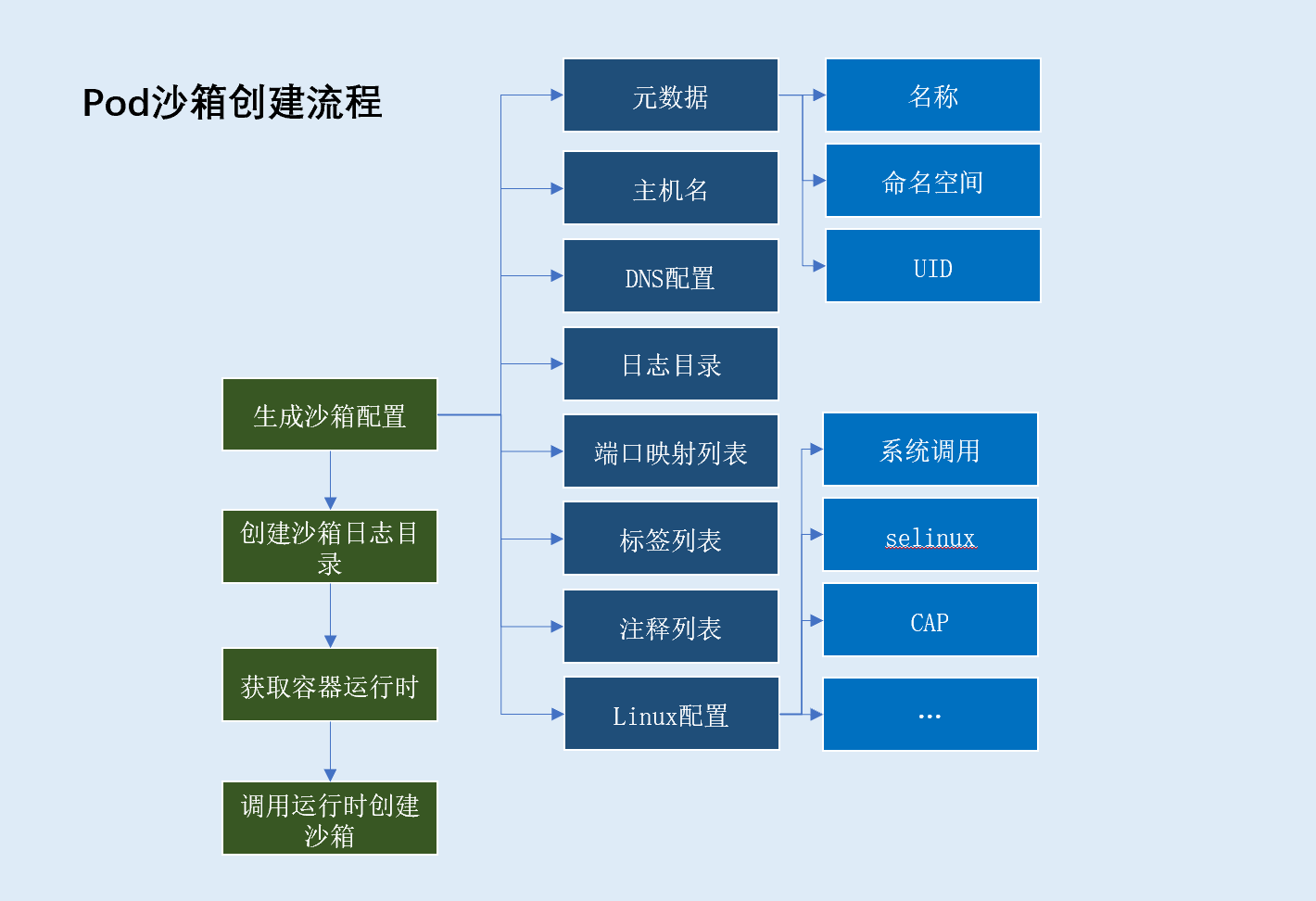
pod沙箱创建流程
流程解析
pod沙箱创建流程,主要分为以下步骤:
- 生成沙箱容器配置,配置包含:
- 沙箱元数据(基于元数据生成沙箱唯一标识)
pod沙箱名称(取值pod名称)pod沙箱命名空间(取值pod命名空间)uid(取值pod uid)
pod沙箱主机名(一般取值pod名称)pod沙箱日志目录pod沙箱DNS配置(DNS server、search domain)pod沙箱端口映射列表(遍历pod下容器端口映射获得)pod沙箱标签集合pod定义标签:metadata.labels字段kubelet注入标签:io.kubernetes.pod.name、io.kubernetes.pod.namespace、io.kubernetes.pod.uid
pod沙箱注释集合:metadata.annonations字段linux相关配置: 系统调用、SELinuxOptions等创建
pod沙箱日志目录(/var/log/pods/<pod namespace>_<pod name>_<pod uid>)- 获取容器运行时
- 根据
pod容器运行时、pod沙箱配置创建pod沙箱
源码解析
kubernetes\pkg\kubelet\kuberuntime\kuberuntime_sandbox.go
func (m *kubeGenericRuntimeManager) createPodSandbox(pod *v1.Pod, attempt uint32) (string, string, error) {
podSandboxConfig, err := m.generatePodSandboxConfig(pod, attempt)
if err != nil {
message := fmt.Sprintf("GeneratePodSandboxConfig for pod %q failed: %v", format.Pod(pod), err)
klog.Error(message)
return "", message, err
}
// Create pod logs directory
err = m.osInterface.MkdirAll(podSandboxConfig.LogDirectory, 0755)
if err != nil {
message := fmt.Sprintf("Create pod log directory for pod %q failed: %v", format.Pod(pod), err)
klog.Errorf(message)
return "", message, err
}
runtimeHandler := ""
if utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.RuntimeClass) && m.runtimeClassManager != nil {
runtimeHandler, err = m.runtimeClassManager.LookupRuntimeHandler(pod.Spec.RuntimeClassName)
if err != nil {
message := fmt.Sprintf("CreatePodSandbox for pod %q failed: %v", format.Pod(pod), err)
return "", message, err
}
if runtimeHandler != "" {
klog.V(2).Infof("Running pod %s with RuntimeHandler %q", format.Pod(pod), runtimeHandler)
}
}
podSandBoxID, err := m.runtimeService.RunPodSandbox(podSandboxConfig, runtimeHandler)
if err != nil {
message := fmt.Sprintf("CreatePodSandbox for pod %q failed: %v", format.Pod(pod), err)
klog.Error(message)
return "", message, err
}
return podSandBoxID, "", nil
}
从上面代码中我们发现有个RuntimeClass特性,这个特性是干嘛的?
RuntimeClass是什么?
背景介绍
Kubernetes最初是为了支持在Linux主机上运行本机应用程序的Docker容器而创建的。
从Kubernetes 1.3中的rkt开始,更多的运行时间开始涌现,这导致了容器运行时接口(Container Runtime Interface)(CRI)的开发。
从那时起,备用运行时集合越来越大:为了加强工作负载隔离,Kata Containers和gVisor等项目被发起,并且Kubernetes对Windows的支持正在稳步发展。
由于存在诸多针对不同用例的运行时,集群对混合运行时的需求变得明晰起来。但是,所有这些不同的容器运行方式都带来了一系列新问题要处理:
- 用户如何知道哪些运行时可用,并为其工作负载选择运行时?
- 我们如何确保将
Pod被调度到支持所需运行时的节点上? - 哪些运行时支持哪些功能,以及我们如何向用户显示不兼容性?
- 我们如何考虑运行时的各种资源开销?
RuntimeClass旨在解决这些问题。
什么场景需要多个运行时?
举个例子,有一个开放的云平台向外部用户提供容器服务,平台上运行有两种容器,一种是云平台管理用的容器(可信的),一种是用户部署的业务容器(不可信)。
在这种场景下,我们希望使用runc运行可信容器(弱隔离但性能好),用runv运行不可信容器(强隔离安全性好)。
值得注意的是:
RuntimeClass是Pod级别的概念(即同一pod内容器的运行时必须相同)
为什么RuntimeClass是Pod级别的概念?
Kubernetes资源模型期望Pod中的容器之间可以共享某些资源。如果Pod由具有不同资源模型的不同容器组成,支持必要水平的资源共享变得非常具有挑战性。
例如,要跨VM边界支持本地回路(localhost)接口非常困难,但这是Pod中两个容器之间通信的通用模型。
如何使用
RuntimeClass
- 在
Kubernetes worker节点配置CRI shim
例如CRI-O运行时的配置,需要在文件/etc/crio/crio.conf定义runtime的handler_name
[crio.runtime.runtimes.${HANDLER_NAME}]
runtime_path = "${PATH_TO_BINARY}"
- 创建
RuntimeClass资源对象;
$ cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: node.k8s.io/v1beta1 # RuntimeClass is defined in the node.k8s.io API group
kind: RuntimeClass
metadata:
name: myclass # The name the RuntimeClass will be referenced by
# RuntimeClass is a non-namespaced resource
handler: myconfiguration # The name of the corresponding CRI configuration
EOF
- 在
pod中指定RuntimeClass
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: mypod
spec:
runtimeClassName: myclass
# ...
docker运行时下创建启动pod沙箱的具体流程
上文中我们已经拥有了创建pod沙箱所需的配置,接下来我们针对docker运行时下,创建启动pod沙箱的流程做进一步分析
docker运行时下,pod沙箱实质是由一个包含该pod的网络名称空间的容器实现的。
创建启动流程如下:
- 拉取
pod沙箱所需镜像(即pause容器镜像,默认k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.2) - 根据配置调用运行时创建沙箱容器(即
pause容器) - 创建沙箱容器检查端点(pod下容器的端接口映射列表)
- 启动沙箱容器,如果启动失败将被回收。启动成功后重写
docker生成的/etc/resolv.conf文件 - 设置沙箱容器网络: 如果
pod共享主机网络命名空间,则跳过后续流程直接返回。此时创建启动pod沙箱流程结束。
源码解析
kubernetes\pkg\kubelet\dockershim\docker_sandbox.go
func (ds *dockerService) RunPodSandbox(ctx context.Context, r *runtimeapi.RunPodSandboxRequest) (*runtimeapi.RunPodSandboxResponse, error) {
config := r.GetConfig()
// Step 1: Pull the image for the sandbox.
image := defaultSandboxImage
podSandboxImage := ds.podSandboxImage
if len(podSandboxImage) != 0 {
image = podSandboxImage
}
// NOTE: To use a custom sandbox image in a private repository, users need to configure the nodes with credentials properly.
// see: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/images/#configuring-nodes-to-authenticate-to-a-private-repository
// Only pull sandbox image when it's not present - v1.PullIfNotPresent.
if err := ensureSandboxImageExists(ds.client, image); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Step 2: Create the sandbox container.
if r.GetRuntimeHandler() != "" && r.GetRuntimeHandler() != runtimeName {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("RuntimeHandler %q not supported", r.GetRuntimeHandler())
}
createConfig, err := ds.makeSandboxDockerConfig(config, image)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to make sandbox docker config for pod %q: %v", config.Metadata.Name, err)
}
createResp, err := ds.client.CreateContainer(*createConfig)
if err != nil {
createResp, err = recoverFromCreationConflictIfNeeded(ds.client, *createConfig, err)
}
if err != nil || createResp == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to create a sandbox for pod %q: %v", config.Metadata.Name, err)
}
resp := &runtimeapi.RunPodSandboxResponse{PodSandboxId: createResp.ID}
ds.setNetworkReady(createResp.ID, false)
defer func(e *error) {
// Set networking ready depending on the error return of
// the parent function
if *e == nil {
ds.setNetworkReady(createResp.ID, true)
}
}(&err)
// Step 3: Create Sandbox Checkpoint.
if err = ds.checkpointManager.CreateCheckpoint(createResp.ID, constructPodSandboxCheckpoint(config)); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Step 4: Start the sandbox container.
// Assume kubelet's garbage collector would remove the sandbox later, if
// startContainer failed.
err = ds.client.StartContainer(createResp.ID)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to start sandbox container for pod %q: %v", config.Metadata.Name, err)
}
// Rewrite resolv.conf file generated by docker.
// NOTE: cluster dns settings aren't passed anymore to docker api in all cases,
// not only for pods with host network: the resolver conf will be overwritten
// after sandbox creation to override docker's behaviour. This resolv.conf
// file is shared by all containers of the same pod, and needs to be modified
// only once per pod.
if dnsConfig := config.GetDnsConfig(); dnsConfig != nil {
containerInfo, err := ds.client.InspectContainer(createResp.ID)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to inspect sandbox container for pod %q: %v", config.Metadata.Name, err)
}
if err := rewriteResolvFile(containerInfo.ResolvConfPath, dnsConfig.Servers, dnsConfig.Searches, dnsConfig.Options); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("rewrite resolv.conf failed for pod %q: %v", config.Metadata.Name, err)
}
}
// Do not invoke network plugins if in hostNetwork mode.
if config.GetLinux().GetSecurityContext().GetNamespaceOptions().GetNetwork() == runtimeapi.NamespaceMode_NODE {
return resp, nil
}
// Step 5: Setup networking for the sandbox.
// All pod networking is setup by a CNI plugin discovered at startup time.
// This plugin assigns the pod ip, sets up routes inside the sandbox,
// creates interfaces etc. In theory, its jurisdiction ends with pod
// sandbox networking, but it might insert iptables rules or open ports
// on the host as well, to satisfy parts of the pod spec that aren't
// recognized by the CNI standard yet.
cID := kubecontainer.BuildContainerID(runtimeName, createResp.ID)
networkOptions := make(map[string]string)
if dnsConfig := config.GetDnsConfig(); dnsConfig != nil {
// Build DNS options.
dnsOption, err := json.Marshal(dnsConfig)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to marshal dns config for pod %q: %v", config.Metadata.Name, err)
}
networkOptions["dns"] = string(dnsOption)
}
err = ds.network.SetUpPod(config.GetMetadata().Namespace, config.GetMetadata().Name, cID, config.Annotations, networkOptions)
if err != nil {
errList := []error{fmt.Errorf("failed to set up sandbox container %q network for pod %q: %v", createResp.ID, config.Metadata.Name, err)}
// Ensure network resources are cleaned up even if the plugin
// succeeded but an error happened between that success and here.
err = ds.network.TearDownPod(config.GetMetadata().Namespace, config.GetMetadata().Name, cID)
if err != nil {
errList = append(errList, fmt.Errorf("failed to clean up sandbox container %q network for pod %q: %v", createResp.ID, config.Metadata.Name, err))
}
err = ds.client.StopContainer(createResp.ID, defaultSandboxGracePeriod)
if err != nil {
errList = append(errList, fmt.Errorf("failed to stop sandbox container %q for pod %q: %v", createResp.ID, config.Metadata.Name, err))
}
return resp, utilerrors.NewAggregate(errList)
}
return resp, nil
}
设置沙箱容器网络流程解析: 调用
CNI进行pod网络配置
kubernetes下容器网络由CNI管理,而非容器运行时。
CNI负责分配pod ip,在沙箱中设置路由,创建接口等。理论上,它的管辖范围仅限于pod沙箱网络,但它也可能在主机上插入iptables规则或开放端口,以满足CNI标准还不认可的pod规范的部分。